Manipulateurs à degrés de liberté complexes/Robots with complex DOF
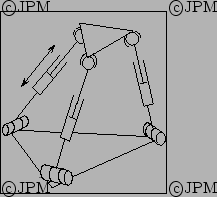
Le
manipulateur à 3 degrés de liberté de Lee. Les articulations des
segments avec la base sont , disposées à 120 degrés.
Les articulations avec le plateau mobile sont des rotules et des actionneurs
prismatiques permettent de faire varier la longueur des segments. Les
degrés de liberté sont des translations sur l'axe vertical et les angles de précession
et de nutation, d'après Lee [102].
Lee mechanism: a link of this mechanism is constituted (from the base to the platform) by a passive revolute joint, an actuated prismatic joint and a ball-and-socket joint.
Lee mechanism: a link of this mechanism is constituted (from the base to the platform) by a passive revolute joint, an actuated prismatic joint and a ball-and-socket joint.
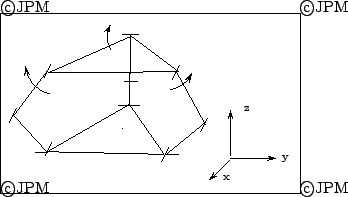
Une variante du mécanisme de Lee, le robot
HALF [109,110]. Les actionneurs prismatiques
sont remplacés par des actionneurs rotatifs. Les mouvements
possibles sont la rotation autour de y et les translation en y,z.
A variant of Lee mechanism: the linear actuator are substituted by
rotary one and a specific geometry allow to have rotation around the y
axis and translation along the y, z axis
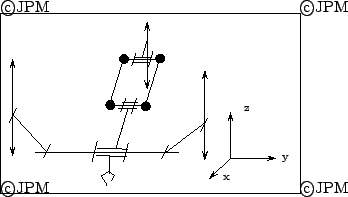
Une autre variante du
HALF [111]. Les actionneurs sont prismatiques
et les mouvements
possibles sont la rotation autour de y et les translation en y,z.
A variant of the HALF robot: the actuators are linear
and a specific geometry allow to have rotation around the y
axis and translation along the y, z axis
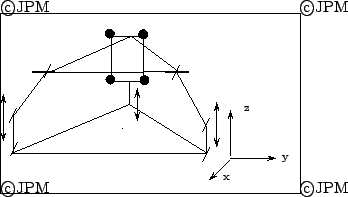
Une autre variante du mécanisme de Lee où les actionneurs rotatifs
sont remplacés par des prismatiques[2]. Les mouvements
possibles sont la rotation autour de y et les translation en y,z.
A variant of Lee mechanism: the revolute actuator are substituted by
linear one and a specific geometry allow to have rotation around the y
axis and translation along the y, z axis
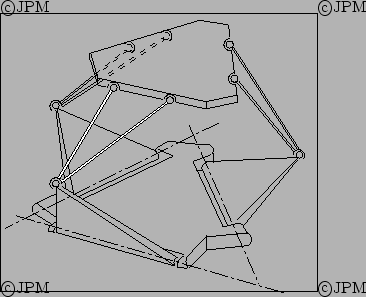
Une structure proposée par Lambert.
Les triangles
articulés
proches de la base sont motorisés, d'après
Lambert [96].
A structure proposed by Lambert: the revolute joints connected to the base are actuated.
A structure proposed by Lambert: the revolute joints connected to the base are actuated.
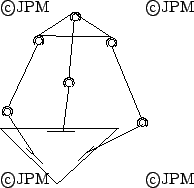
L'équivalent de Dunlop où les articulations
proches de la base sont motorisés, d'après
Dunlop [37].
A mechanism equivalent to the previous mechanism.
A mechanism equivalent to the previous mechanism.
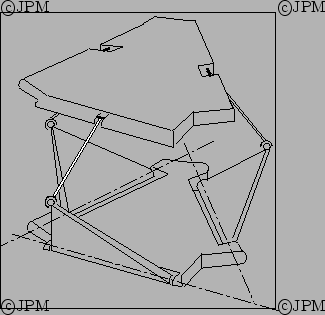
(d'après [73]).
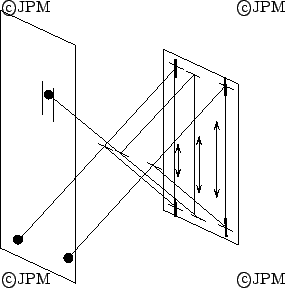
Le mécanisme de Chung à base de 4 barres qui permet d'avoir un
degré de liberté en translation et 2 en rotation
(d'après [28]).
A four-bar based robot, allowing one translational dof and two rotations
Une variante qui permet d'avoir un mouvement cylindrique: rotation
autour de y, translation selon y, z (d'après [174])
An equivalent that allow to have cylindrical motion: rotation around
y, translation along y,z
Une variante qui permet d'avoir un mouvement cylindrique: rotation
autour de y, translation selon y, z (d'après [118,79]),
utilisé par Fatronik pour la machine-outil VERNE
An equivalent that allow to have cylindrical motion: rotation around
y, translation along y,z, used in the VERNE machine-tool
Le mécanisme de Ceccarelli: les mécanismes à 4 barres
sont actionnés et modifie la position d'une articulation
prismatique qui est liée au plateau mobile par une
rotule (d'après [24]).
Ceccarelli mechanism: the four-bars mechanism are actuated and are used to modify the position of a passive prismatic joint which is connected to the moving platform by a ball-and-socket joint.
Ceccarelli mechanism: the four-bars mechanism are actuated and are used to modify the position of a passive prismatic joint which is connected to the moving platform by a ball-and-socket joint.
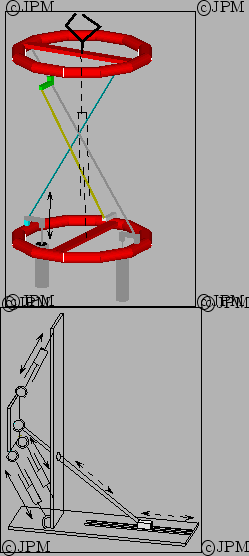
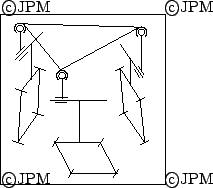
Robots à 3 degrés de liberté
avec des contraintes passives. En haut et au milieu
les vérins assurent un déplacement des
points d'articulation. La rotation autour de la normale au plateau
mobile est obtenue par une tige articulée avec des cardans, libre selon
son axe, d'après Lande [97].
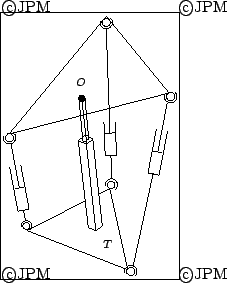
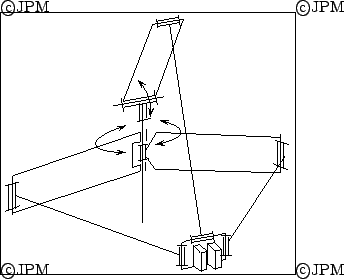
Une architecture proposée par Reboulet. La barre  ,
reliée
à la
base par un cardan en
,
reliée
à la
base par un cardan en  , est extensible mais ne peut tourner
autour de son axe, d'après Reboulet [144].
, est extensible mais ne peut tourner
autour de son axe, d'après Reboulet [144].
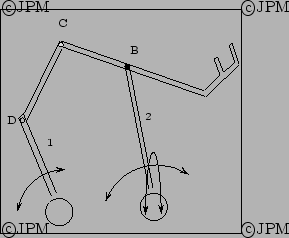
Le robot à 3 degrés de liberté de Stoughton, d'après
Stoughton [164].
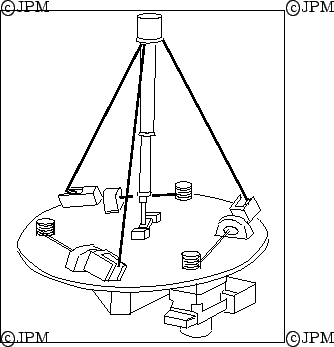
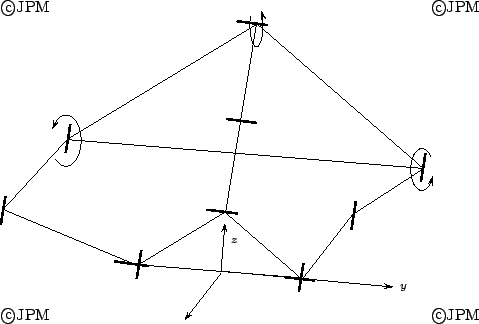
Le robot à 3 degrés de liberté de Landsberger: les segments
sont des câbles qui peuvent s'enrouler sur des tambours. La tension
des câbles est assurée par le mât central qui exerce une poussée
passive vers le haut, d'après Landsberger [98].
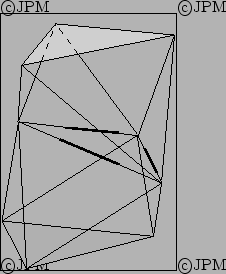
Le robot de Arun.
permettent de modifier les longueurs des côtés de la face triangulaire
commune aux deux octaèdres, d'après Arun [8].
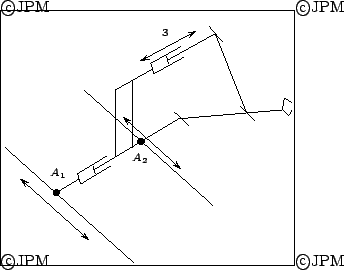
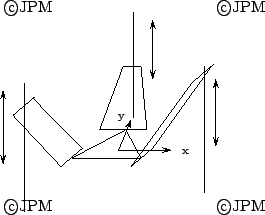
Le mécanisme de translation de Cheng.
Les translations des points 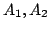 permettent de placer l'organe terminal dans une position
quelconque dans un plan alors que l'actionneur 3 permet de changer
son élévation (d'après [27])
permettent de placer l'organe terminal dans une position
quelconque dans un plan alors que l'actionneur 3 permet de changer
son élévation (d'après [27])
Cheng mechanism: the translation of points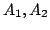 enable to put the
end-effector center anywhere in a plane while actuator 3 enable to
change its elevation
enable to put the
end-effector center anywhere in a plane while actuator 3 enable to
change its elevation
Cheng mechanism: the translation of points
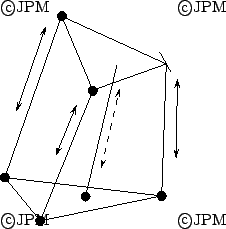
Le
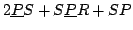 de Lu [113].
La jambe centrale et l'articulation
de Lu [113].
La jambe centrale et l'articulation 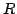 imposent que les degrés de liberté soient une translation selon
l'axe de la jambe et deux orientations.
imposent que les degrés de liberté soient une translation selon
l'axe de la jambe et deux orientations.
The central passive leg and the 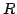 joint impose that the end-effector
platform d.o.f. are a translation along the leg and two orientations.
joint impose that the end-effector
platform d.o.f. are a translation along the leg and two orientations.
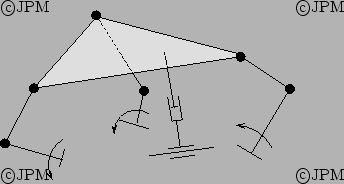
Une variante: le robot 3-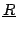 SS+CP de
Hess-Coelho [68]. Le mât central est articulé
sur une articulation passive cylindrique et posséde une articulation
prismatique passive.
SS+CP de
Hess-Coelho [68]. Le mât central est articulé
sur une articulation passive cylindrique et posséde une articulation
prismatique passive.
A variant: the 3-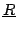 SS+CP. The central mast is connected
to the base by a passive cylindrical joint and has a passive prismatic
joint.
SS+CP. The central mast is connected
to the base by a passive cylindrical joint and has a passive prismatic
joint.
Une robot de type
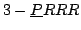 , avec 3 degrés de
liberté: une translation et deux rotations [148].
, avec 3 degrés de
liberté: une translation et deux rotations [148].
A
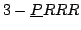 robot with 3 degrees of
freedom: one translation and two rotations
robot with 3 degrees of
freedom: one translation and two rotations

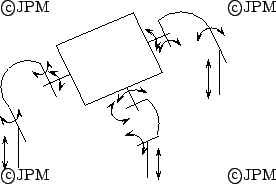
Une robot avec 3 degrés de
liberté: deux translations et une rotation [187].
A robot with 3 degrees of
freedom: two translations and one rotation