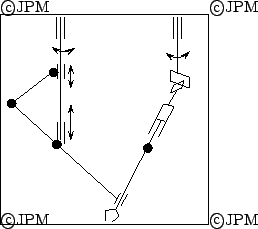
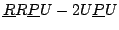Manipulateurs à 4 degrés de liberté/4 DOF robots
un manipulateur à 4 degrés de liberté utilisé
pour un simulateur de vol. Une contrainte passive
assure que les seuls degrés de liberté sont les rotations et une translation selon
l'axe 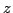 , d'après Koevermans [88].
, d'après Koevermans [88].
Here a passive kinematic chain imposes that one point of the platform translates along the vertical axis while the platform could then only rotate around this point.
Here a passive kinematic chain imposes that one point of the platform translates along the vertical axis while the platform could then only rotate around this point.
un manipulateur à 4 degrés de liberté. Une contrainte passive
assure que les seuls degrés de liberté sont les rotations et une translation selon
l'axe 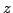 , d'après Gallardo [46].
, d'après Gallardo [46].
Here a kinematic chain imposes that one point of the platform translates along the vertical axis while the platform could then only rotate around this point.
Here a kinematic chain imposes that one point of the platform translates along the vertical axis while the platform could then only rotate around this point.
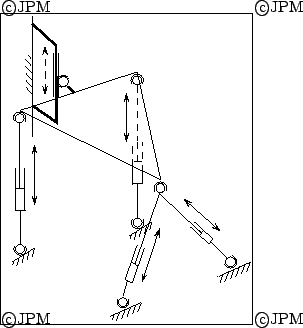
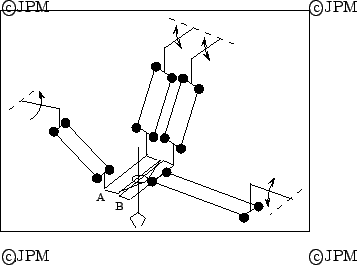
Un robot à 4 degrés de liberté proposé
dans le cadre du projet VAP:
trois rotations
autour de la rotule 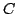 et une translation selon l'axe
et une translation selon l'axe  . Le mât central
est libre selon cet axe, d'après Reboulet [145].
. Le mât central
est libre selon cet axe, d'après Reboulet [145].
A 4-dof robot proposed in the framework of the VAP project (Vehicule Autonome Planetaire=Autonomous planetary vehicle). The dof are the rotation around the ball-and-socket joint at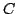 and a translation
along the
and a translation
along the 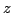 axis. The central mast passive joint enable this translation.
axis. The central mast passive joint enable this translation.
A 4-dof robot proposed in the framework of the VAP project (Vehicule Autonome Planetaire=Autonomous planetary vehicle). The dof are the rotation around the ball-and-socket joint at
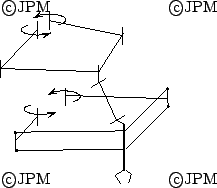
Dans l'exemple précédent l'articulation prismatique passive peut
être remplacé par 2 articulations R [185]
In the previous example the P passive joint may be sustituted by 2 R
joints.
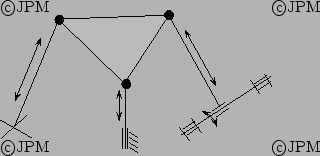
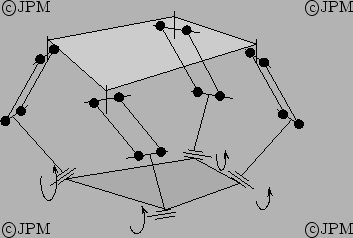
Une autre variante de type 3-SPU+UPR [112], qui fournit 3
degrés de liberté en orientation et la translation selon l'axe 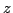 .
.
Another variant based on a 3-SPU+UPR architecture, providing 3 dof in
rotation and a translation along the 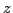 axis.
axis.
Le manipulateur de Rebman utilisant des tiges
déformables, d'après Rebman [143].
Rebman robot with flexible beams.
Rebman robot with flexible beams.
Un manipulateur avec trois chaînes, d'après
Tanev [165].
A robot with three kinematic chains.
A robot with three kinematic chains.
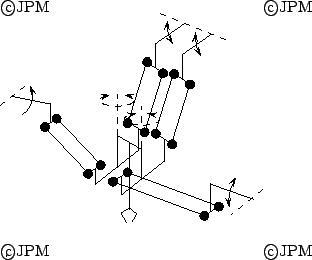
Un robot hybride, d'après [70].
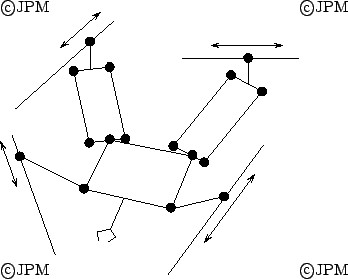
Une variante du H4, le Quadriglide. A variant of the H4, the Quadriglide
[5]
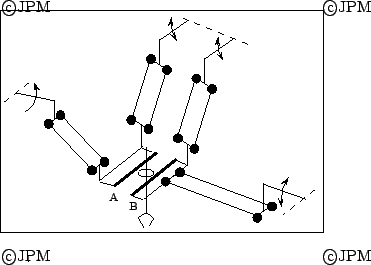
Le robot I4 de Krut. C'est une robot de la famille H4 mais la
rotation de l'organe terminal est obtenu différemment. Ici les
parties A et B peuvent se translater l'une par rapport à l'autre et
un mécanisme à pignon-crémaillère permet de convertir cette rotation en
rotation de l'organe terminal [94]
The I4 robot of Krut. It belong to the family of the H4 but the
orientation of the end-effector uses another principle. Part a and B
are free to translate along one direction with respect to each other:
a rack and pinion mechanism allows to convert this translation into a rotation
of the end-effector
Le robot I4R de Krut, une variante du I4.
Un mécanisme à poulie permet de convertir cette rotation en
rotation de l'organe terminal [95]
The I4R robot of Krut,a variant of the I4.
A pulley mechanism allows to convert this translation into a rotation
of the end-effector
Le robot DUAL4 de Pierrot: le mouvement plan des bras supérieurs
permet le contrôle du mouvement vertical et de la rotation autour de
cet axe [138]
The DUAL4 robot of Pierrot: the motion of the upper legs allow to
control the vertical translation and the rotation around this axis
Ce robot présente des chaînes constituées à partir de la
base de 2 articulations R, un parallélogramme, puis à nouveau 2
articulations R. Il propose 3 ddl en translation et une rotation
autour de la normale à la plate-forme.
This robot has chains constituted of (from the base) 2 R joints, a parallelogram and 2 R joints connected to the platform [83]. It has 3 translational dof and a rotation around the axis normal to the platform.
This robot has chains constituted of (from the base) 2 R joints, a parallelogram and 2 R joints connected to the platform [83]. It has 3 translational dof and a rotation around the axis normal to the platform.
Le robot HITA-STT de Clavel, the HITA-STT from
Clavel [29]
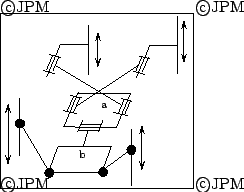
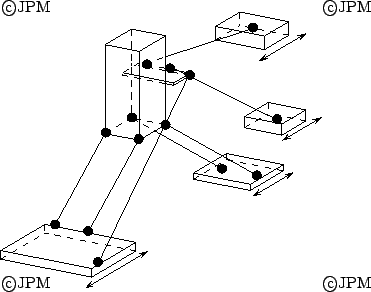
Le manipulateur à 4 degrés de liberté de
Chen [25]. La partie (a) de l'organe terminal est
connecté par des articulations rotoïdes passives à des
actionneurs prismatiques à axe vertical. Les degrés de liberté
de cette partie sont des translations selon y,z et une rotation autour
de x. La partie (b) est connectée à (a) par une articulation
rotoïde et a donc un degré de liberté supplémentaire qui
est contrôlée par le mouvement de deux actionneurs prismatiques
reliés à (b) par des rotules.
Part (a) of this mechanism is connected through revolute joints to two
linear actuators. This part has 3 dof (translation along y and z,
rotation around x). Part (b) of the end effector is connected to (a)
through a revolute joint and has one more dof. This dof and the motion
of (a) are obtained by two linear actuators connected to (b) through
ball-and-socket joints.
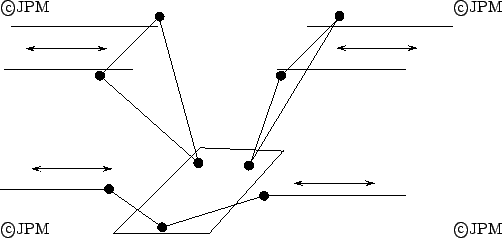
Un manipulateur à 4 degrés de liberté de
Chen [26]. D'un point du géométrique son
équivalent est 2-SPS 2-RS et a deux degré de libertéen translation et 2 degré de libertéen
rotation.
This robot is equivalent to a 2-SPS 2-RS mechanism and has 2
translational and 2 rotational dof.
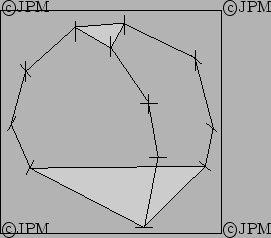
Le robot de Li avec seulement des articulations rotoïdes. Les
degrés de liberté sont les 3 translations et une rotation autour
de la normale de la plate-forme [103]
A 4 dof robot with only revolute joints. The dof are the three
translations and a rotation around the normal of the platform
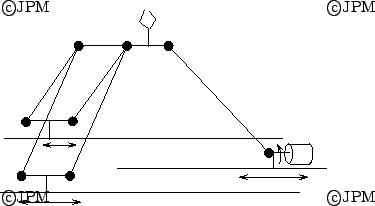
The Manta robot with 3 translations and one rotation [151]
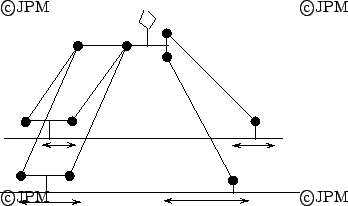
The Kanuk robot with 3 translations and one rotation [151]
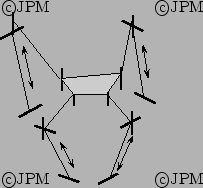
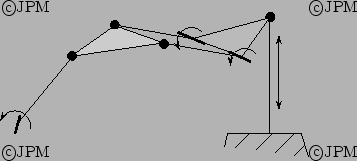
Un robot à 4 degré de liberté de type 4-RPRRR [104]
Seul les translations et la rotation autour de la normale à la
plate-forme sont possibles.
Only translation and rotation around the normal to the platform are
possible.
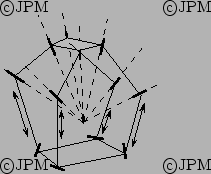
Un robot à 4 degré de liberté de type 4-RPUR [104]
Seul les rotations de la plate-forme sont possibles ainsi qu'une
translation selon z
Only rotation of the platform and a translation along the z axis are
possible.
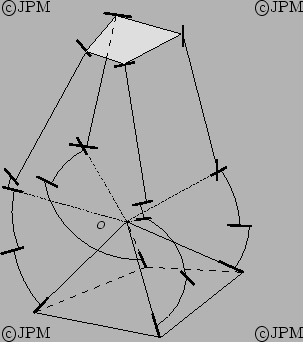
Un robot 1T-3R de type 4-5R. Les mouvements possibles sont une
rotation autour de O ainsi qu'une translation selon la normale à la plate-forme [189]
A 4 d.o.f. robot: the possible motion are the 3 rotations around O and
a translation along the platform normal.
A 4-dof robot with two platforms [3]
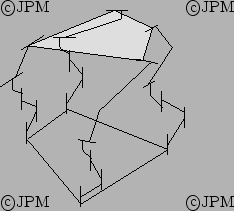
One of the many 3T-1R robot proposed by the team of Gosselin, here by Kong [92]
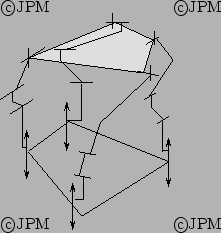
Another 3T-1R robot, called the Quadrupteron, proposed by the team of
Gosselin, here of type
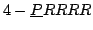 , proposed by Richard [150]
, proposed by Richard [150]
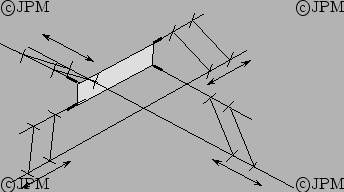
Un autre robot 3T-1R utilisant 4 parallélogrammes qui sont
translatés par des actionneurs linéaires [156].
Another 3T-1R robot that uses 4 parallelograms whose base is
translated by 4 linear actuators.
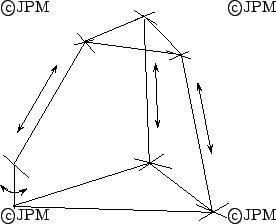
Un autre robot 3T-1R de type
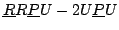 [114].
[114].
Another 3T-1R robot of type