|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Design Design |
 Boxes Boxes |
 Combinator Combinator |
 Formatting Formatting |
 Geometry Geometry |
 Reuse Reuse |
 Selections Selections |
 Paths Paths |
 Concurrency Concurrency |
 Exception Exception |
 Interaction Interaction |
 Utility Utility |
 Resource Resource |
 Drawing Drawing |
 Incremental Incremental |
 Customize Customize |
 Various Various |
Exceptions Management
The API cross references![]() give an immediate access to relevant interfaces and classes.
give an immediate access to relevant interfaces and classes.
 Errors
Errors
An error indicates serious problems that an application should not try to catch.
 Exceptions
Exceptions
An exception indicates problems that an application might want to catch.
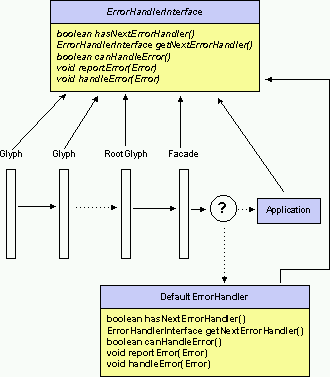
 Error Handler
Error Handler
An error handler implements a chain of responsibility
to deal with bug report and warning. Each member of the
chain knows how to access its successor and how to handle
a request. This scheme is a flexible way to adapt error
management to a specific application. The default error
handler reports bugs by throwing an error and writes
warning on the standard error output stream![]() .
In the case of a broken chain of responsability, we
delegate the request to the
DefaultErrorHandler class variable
.
In the case of a broken chain of responsability, we
delegate the request to the
DefaultErrorHandler class variable![]() .
.
Here is the
reason![]() we do not rely on exception to propagate errors.
we do not rely on exception to propagate errors.
 API Cross References
API Cross References
- Interfaces:
- Classes:
- Exceptions:
 Design Design |
 Boxes Boxes |
 Combinator Combinator |
 Formatting Formatting |
 Geometry Geometry |
 Reuse Reuse |
 Selections Selections |
 Paths Paths |
 Concurrency Concurrency |
 Exception Exception |
 Interaction Interaction |
 Utility Utility |
 Resource Resource |
 Drawing Drawing |
 Incremental Incremental |
 Customize Customize |
 Various Various |
|
Comments or suggestions? Need some help? Copyright ©1998 INRIA Last updated 5 October 1998 by Bruno Conductier |
|