Keywords
Near-wall particle motion (sliding / rolling / lift), particle-surface adhesion, surface roughness, avalanche effects.

Near-wall particle motion (sliding / rolling / lift), particle-surface adhesion, surface roughness, avalanche effects.
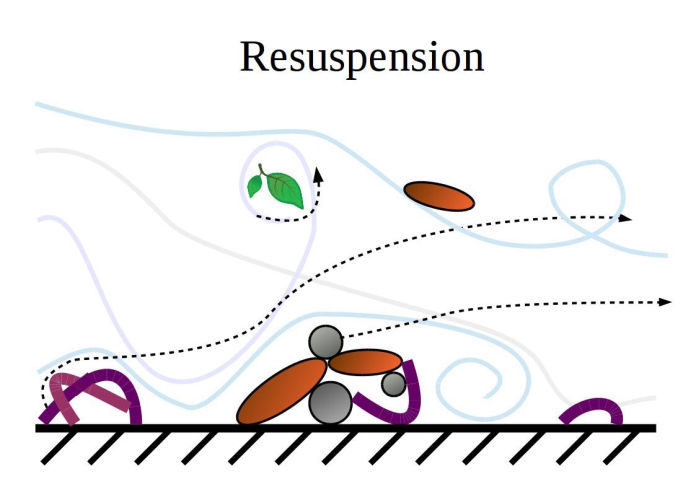
Particle resuspension is concerned with how particles adhering to a surface are detached from a surface and re-entrained into the flow.
The usual measure is a resuspension rate (units in 1/s), which corresponds to the mass of resuspended particles per unit time and per unit surface divided by the surface concentration.
Particles resuspension occurs are in a range of environmental and industrial situations, including:
+ Sand resuspension from dunes (responsible for sand dune dynamics and also related to the transport of sand across oceans)
+ Resuspension of dust in ventilation systems
+ Walking-induced resuspension of contaminated aerosols in hospitals
+ Resuspension of sediments in rivers
The resuspension of a particle adhering to a surface results from a rupture of balance between the forces that tend to move the particle (e.g. hydrodynamic drag or lift) and the forces preventing its motion (surface adhesion, contact friction, buoyancy).
This web page was built with Mobirise