Keywords
Particle collision, particle adhesion, aggregate morphology, particle growth.

Particle collision, particle adhesion, aggregate morphology, particle growth.
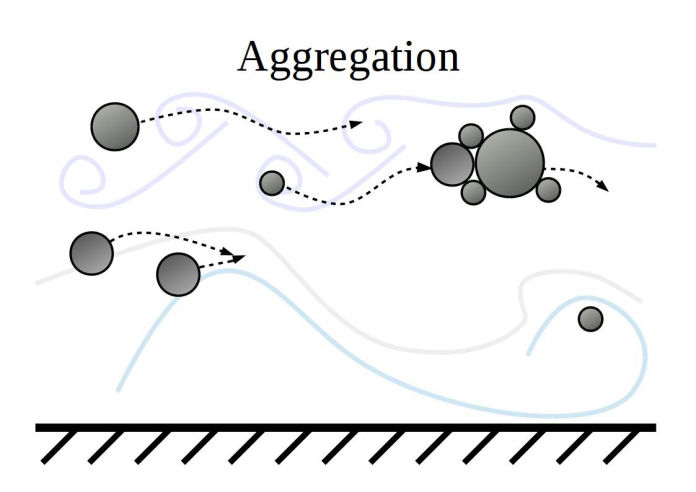
Particle agglomeration is concerned with how particles collide and adhere to each other in a fluid, thus forming larger structures called "aggregates". Depending on the field of research, particle agglomeration is also referred to as aggregation (for solid materials), coalescence (for droplets/bubbles), coagulation (non-Newtonian fluids) or floculation (polymers).
The usual measure is the mean aggregate size in suspension at a given time.
Particles aggregation has implications in a wide range of situations, including environmental & industrial applications such as:
+ Silt agglomeration leading to the formation of river deltas in geomorphology
+ Droplet growth within clouds in meteorology
+ Growth of planetoids in astrophysics
+ Flocculation of impurities in waster-water treatment facilities.
A particle agglomerate with another one in a two-step process:
+ the two particles are first brought in close proximity by the fluid (transport step);
+ particles can stick together if particle-particle interactions do not prevent it (attachment step).
How to build a website - Read more