|
realroot_doc 0.1.1
|
|
realroot_doc 0.1.1
|
#include <univariate_bounds.hpp>
Cauchy bound.
Definition at line 162 of file univariate_bounds.hpp.
| C lower_bound | ( | const Poly & | f | ) | const [inline] |
Computes the Cauchy lower bound on the first positive root as a power of 2.
| C | type of the result. |
| Poly | type of the polynomial. |
| p | Univariate polynomial |
Definition at line 210 of file univariate_bounds.hpp.
References mmx::abs(), mmx::bit_size(), mmx::degree(), and mmx::sign().
{
using univariate::degree;
typedef C RT;
long deg = degree( f);
long l = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= deg; ++i) {
if ( sign( f[i]) * sign( f[0]) < 0 ) {
++l;
}
}
long ba0 = bit_size(f[0]) - 1; /* puiss de 2 < an */
bool bound_set = false;
long K = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= deg; ++i) {
if ( sign( f[i]) * sign( f[0]) < 0 ) {
long bai = bit_size( RT( l * f[i])) - 1;
long p = bai - ba0 - 1 ;
long k = i;
long q = p / k;
long r = p % k;
long rq = 0;
if (r <= k-2) {
rq = q + 1;
} else {
rq = q + 2;
}
if ( (bound_set == false) || (K < rq) ) {
K = rq;
bound_set = true;
}
}
}
if ( K < 0 ) {return pow2<RT>( abs( K) );}
return 0;
}
| long lower_power_2 | ( | const Poly & | f | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 256 of file univariate_bounds.hpp.
References mmx::abs(), mmx::bit_size(), mmx::degree(), and mmx::sign().
{
using univariate::degree;
typedef typename Poly::value_type RT;
long deg = degree( f);
long l = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= deg; ++i) {
if ( sign( f[i]) * sign( f[0]) < 0 ) {
++l;
}
}
long ba0 = bit_size(f[0]) - 1; /* puiss de 2 < an */
bool bound_set = false;
long K = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= deg; ++i) {
if ( sign( f[i]) * sign( f[0]) < 0 ) {
long bai = bit_size( RT( l * f[i])) - 1;
long p = bai - ba0 - 1 ;
long k = i;
long q = p / k;
long r = p % k;
long rq = 0;
if (r <= k-2) {
rq = q + 1;
} else {
rq = q + 2;
}
if ( (bound_set == false) || (K < rq) ) {
K = rq;
bound_set = true;
}
}
}
if ( K < 0 ) { abs( K);}
return -1;
}
| double upper_bound | ( | const Poly & | p | ) |
Definition at line 305 of file univariate_bounds.hpp.
References mmx::abs(), mmx::univariate::lcoeff(), mmx::vctops::max(), and mmx::numerics::rnd_up().
{
typedef typename Poly::value_type coeff_t;
numerics::rounding<double> rnd( numerics::rnd_up() );
//using std::abs;
coeff_t M=0;
for(unsigned i=0;i< p.size(); i++) M = std::max(M, coeff_t(abs(p[i])));
// abs_max<coeff_t> M = std::for_each(p.begin(), p.end()-1, abs_max<coeff_t>());
coeff_t an = coeff_t(abs(univariate::lcoeff(p)));
//std::cout <<M<<" "<<an<<" "<<std::endl;
double res=as<double>(coeff_t(M/an)) + 1;
// std::cout <<res<<std::endl;
return res;
}
| static C upper_bound | ( | const Poly & | p | ) | [inline, static] |
Computes the Cauchy root bound.
| C | type of the result. |
| Poly | type of the polynomial. |
| p | Univariate polynomial |
If the polynomial @ is in the monomial basis is of the form
![\[ p(x) = a_{0} + a_{1} x+ \cdots + a_{d}\, x^d, \]](form_19.png)
the Cauchy bound on the modul of the roots of 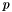 is
is
![\[ 1 + max{|a_{0}|,...,|a_{d-1}|}/|a_{d}| \]](form_20.png)
Definition at line 186 of file univariate_bounds.hpp.
References mmx::abs(), mmx::univariate::lcoeff(), and abs_max< T >::max.
Referenced by mmx::bound_root().
{
// DEBUG::print("Cauchy");
typedef typename Poly::value_type RT;
typedef typename texp::rationalof<RT>::T rational;
//using std::abs;
abs_max<RT> M = std::for_each(p.begin(), p.end()-1, abs_max<RT>());
RT an = abs(lcoeff(p));
// rational val= rational(M.max)/an + rational(1);
C res= C(M.max/an) + C(1);
// C res; let::assign(res, val);
return res;
}