|
realroot_doc 0.1.1
|
|
realroot_doc 0.1.1
|
Module for Univariate POLynomials with a Direct Access Representation. More...
Module for Univariate POLynomials with a Direct Access Representation.
It contains generic implementations on univariate (dense) polynomials. This set of functions apply when R provides the following methods or definitions:
typename R::value_type; typename R::size_type; typename R::iterator; typename R::reverse_iterator; iterator_t R::begin(); iterator_t R::end(); value_type R::operator[](int);
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | ||
| const monomials< C > & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 216 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree().
Referenced by use< operators_of, univariate::monomials< C > >::add(), add(), and div_rem().
{
array::add(r,a,b);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | ||
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 223 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
{
if(degree(a)>-1) {
r=a; r[0]+=c;
}
else
r= Polynomial(c,0);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 234 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
{
if(degree(r)>-1) {
r[0]+=c;
}
else
r= Polynomial(c,0);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 244 of file univariate.hpp.
References add(), and check_degree().
{
array::add(r,a);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::add_cst | ( | R & | r, |
| const S & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 429 of file univariate.hpp.
{ r[0]+=c; }
| int mmx::univariate::check_degree | ( | monomials< C > & | a | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 207 of file univariate.hpp.
Referenced by add(), div(), monomials< C >::monomials(), mul(), and sub().
{
int l = a.degree_;
while(l >=0 && (a.tab_[l]==0)) {l--;}
a.degree_=l;
return a.degree_;
}
| void mmx::univariate::checkdegree | ( | R & | p | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 579 of file univariate.hpp.
Referenced by set_monomial().
{
int d = p.size()-1;
if ( d < 0 ) return;
while ( p[d] == 0 ) d--;
p.resize(d+1);
}
| void mmx::univariate::coeff_modulo | ( | R & | r, |
| const typename R::value_type & | x | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 873 of file univariate.hpp.
{
for ( typename R::iterator i = r.begin(); i != r.end(); *i %= x, ++i ) ;
};
| void mmx::univariate::convertm2b | ( | T & | bz, |
| const P & | p, | ||
| unsigned | size, | ||
| const C & | a, | ||
| const C & | b | ||
| ) |
Convert the representation in the monomial basis to the representation in the Bezier basis of $[a,b]$. The matrix of the change of bases is $(c_{i,j})_{0 i,j d}$ with $c_{i,j}= {{i}{j}}/{{d}{j}}$ if $j i$ and $0$ otherwise.
Definition at line 847 of file univariate.hpp.
References mmx::assign(), scale(), mmx::array::set_cst(), shift(), and mmx::size().
Referenced by binary_sleeve_subdivision< K >::init_pol().
{
typedef typename T::value_type coeff_t;
T pps(p.size());
array::assign(pps,p);
if(a !=0)
shift(pps,pps,a);
scale(pps, pps, C(b-a));
array::set_cst(bz,pps[0]);
int dn=1, nm=1;
for(unsigned j=1; j<size; j++) {
dn *= (size-j); dn/= j;
nm=1;
bz[j] += pps[j]/dn;
for(unsigned i=j+1; i<size; i++) {
nm *= i; nm/= (i-j);
bz[i] += pps[j]*nm/dn;
}
}
}
| int mmx::univariate::degree | ( | const monomials< C > & | a | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 201 of file univariate.hpp.
{ return a.degree_;}
| int mmx::univariate::degree | ( | const R & | p | ) |
Definition at line 194 of file univariate.hpp.
Referenced by add(), diff(), div_rem(), eval_homogeneous(), eval_horner(), eval_horner_idx(), lcoeff(), mmx::min_bound(), mul(), mul_index(), numer(), monomials< C >::operator==(), print(), reciprocal(), shift(), and sub().
{
// std::cout <<"(Using default degree) "<<p<<std::endl;
int i = p.size()-1;
while(i>-1 && p[i]==(typename R::value_type)0) i--;
return i;
}
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::derive | ( | const R | p, |
| typename R::value_type | x | ||
| ) |
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::derive | ( | const R & | Pol, |
| const typename R::value_type & | x | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Return an evaluation of the derivation of an univariate polynomial for the value 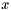 . Example:
. Example:
upoldse<R> p(...);
upoldse<R>::value_type x,d;
d=univariate::derive(p,x);
Definition at line 755 of file univariate.hpp.
References eval().
{
typename R::value_type p,res;
eval(p,res,Pol,x);
return res;
};
| R diff | ( | const R & | p | ) | [inline] |
The derivative of the polynomial p is put in r.
Definition at line 630 of file univariate.hpp.
{
R r(p);
diff(r,p);
return r;
}
| void mmx::univariate::diff | ( | R & | r, |
| const R & | p | ||
| ) | [inline] |
The derivative of the polynomial p is put in r. r should be allocated wi the correct size.
Definition at line 608 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree().
{
int n,i;
r.resize(n=degree(p));
for( i = 1; i < n+1; ++i) r[i-1] =p[i]*i;
}
| void mmx::univariate::div | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | ||
| const monomials< C > & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 330 of file univariate.hpp.
References assert, check_degree(), div_rem(), and Polynomial.
Referenced by use< operators_of, univariate::monomials< C > >::div().
{
assert(&r!=&a);
Polynomial tmp(a);
r = Polynomial(0);
div_rem(r,tmp,b);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::div | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 340 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), div_rem(), and Polynomial.
{
Polynomial tmp(r);
r = Polynomial(0);
div_rem(r,tmp,b);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::div | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 349 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), and mmx::array::div_ext().
{
array::div_ext(r,c);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::div_rem | ( | R & | q, |
| R & | a, | ||
| const R & | b | ||
| ) |
Quotient and remainder of a by b. The polynomial a is modified. At the end of the computation, it is equal to the remainder in the euclidean division. The type R should provide a degree function and a direct access operator.
Definition at line 559 of file univariate.hpp.
References add(), degree(), mul(), and sub().
Referenced by div().
| C mmx::univariate::eval | ( | const R & | p, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 520 of file univariate.hpp.
References eval_horner().
Referenced by derive().
{
return eval_horner(p,c);
}
| void mmx::univariate::eval | ( | O & | p, |
| O & | dp, | ||
| const R & | Pol, | ||
| const I & | x | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Return an evaluation of the polynomial and its derivative at 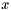 Example:
Example:
upoldse<R> p(...);
upoldse<R>::value_type x,vp,vd;
d=univariate::eval(vp,vd,p,x);
Definition at line 738 of file univariate.hpp.
{
int n = p.size()-1;
p = Pol[n];
dp = O(0);
for ( int j = n-1; j >= 0; dp = dp*x + p, p =p*x + Pol[j], j-- ) ;
};
| C mmx::univariate::eval_homogeneous | ( | const R & | p, |
| const C & | a, | ||
| const C & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 526 of file univariate.hpp.
References mmx::assign(), and degree().
Referenced by mmx::as_interval_data().
{
using namespace let;
C r,y=1,cf;
if(degree(p)>0) {
typedef typename R::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;
const_reverse_iterator it=p.rbegin();
assign(r,*it); it++;
// for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r*=c; assign(cf,*it); r+=cf;}
for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r*=a; y *=b; assign(cf,*it); r=r+cf*y;}
return r;
} else if(degree(p)==0)
{
assign(r,p[0]); return r;
}
else
return C(0);
}
| C mmx::univariate::eval_horner | ( | const R & | p, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 486 of file univariate.hpp.
References mmx::assign(), and degree().
Referenced by eval(), and sign_at().
{
using namespace let;
C r,cf;
if(degree(p)>0) {
typedef typename R::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;
const_reverse_iterator it=p.rbegin();
assign(r,*it); it++;
// for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r*=c; assign(cf,*it); r+=cf;}
for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r=r*c; assign(cf,*it); r=r+cf;}
return r;
} else if(degree(p)>-1)
{
assign(r,p[0]); return r;
}
else
return C(0);
}
| C mmx::univariate::eval_horner_idx | ( | const R & | p, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
| void mmx::univariate::inv_scale | ( | R & | r, |
| const R & | p, | ||
| const C & | l | ||
| ) |
Scale the variable in the polynomial p by l and put the result r. It computes the coefficients of the polynomial 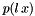 .
.
Definition at line 828 of file univariate.hpp.
Referenced by mmx::inv_scale().
{
int sz=p.size();
r.resize(sz);
sz--;
r[sz]=p[sz];
typename R::value_type s=l;
for(int i=sz-1; i>=0;i--){
r[i]=p[i]*s;
s *=l;
}
}
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::lcoeff | ( | const R & | p | ) | [inline] |
Returns the leading coefficient of the polynomial p.
Definition at line 357 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree().
Referenced by Cauchy< C >::upper_bound().
{
return p[degree(p)];
}
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | R & | a, |
| const R & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 463 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree(), mul_index(), and mmx::array::set_cst().
{
if(degree(a)>=0 && degree(b)>=0)
{
R ta(a);
a.resize(degree(a)+degree(b)+1);
array::set_cst(a,0);
mul_index(a,ta,b);
}
else
array::set_cst(a,0);
}
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | p, | ||
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 311 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), and mul().
{
r=p; mul(r,c); check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | ||
| const monomials< C > & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 287 of file univariate.hpp.
References assert, check_degree(), degree(), mmx::vctops::max(), mul_index(), and mmx::array::set_cst().
Referenced by div_rem(), use< operators_of, univariate::monomials< C > >::mul(), and mul().
{
assert(&r!=&a);
r.resize(std::max(degree(a)+degree(b)+1,0));
array::set_cst(r,(C)0);
mul_index(r,a,b);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Multiplication of a polynomial by a monomial or a scalar.
Definition at line 299 of file univariate.hpp.
References mmx::array::mul_ext().
{
array::mul_ext(r,c);
}
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | a, |
| const monomials< C > & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Multiplication of a polynomial by a polynomial;.
Definition at line 306 of file univariate.hpp.
References mul(), and Polynomial.
{
Polynomial r; mul(r,a,b); a=r;
}
| void mmx::univariate::mul_index | ( | R & | a, |
| const R & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 477 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree(), mul_index(), and mmx::array::set_cst().
{
R ta(a);
a.resize(degree(a)+degree(b)+1);
array::set_cst(a,0);
mul_index(a,ta,b);
}
| void mmx::univariate::mul_index | ( | R & | r, |
| const R & | a, | ||
| const R & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 435 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree(), and Scalar.
Referenced by mul(), and mul_index().
| void mmx::univariate::mul_index_it | ( | R & | r, |
| const R & | a, | ||
| const R & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 446 of file univariate.hpp.
{
typename R::const_iterator ia, ib;
typename R::iterator ir, it;
ir=r.begin();
for (ib=b.begin();ib !=b.end()&& ir != r.end();++ib) {
typename R::value_type c = *ib;
it=ir;
if (c==0) {++ir;continue;}
for (ia=a.begin();ia!=a.end();++ia,++it) {
(*it)+=(*ia)*c;
}
++ir;
}
}
| S mmx::univariate::numer | ( | const R & | f | ) |
Definition at line 878 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree(), mmx::denominator(), mmx::lcm(), and mmx::numerator().
{
S p(0,degree(f));
typename S::value_type d=1;
for(int i=0;i<degree(f)+1;i++) {
if (f[i] !=0) d=lcm(d,denominator(f[i]));
}
for(int i=0;i<degree(f)+1;i++)
p[i]=numerator(f[i])* (d/denominator(f[i]));
return p;
}
| OSTREAM& mmx::univariate::print | ( | OSTREAM & | os, |
| const monomials< C > & | p, | ||
| const VAR & | var | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 376 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree(), and print_as_coeff().
Referenced by print().
{
typedef typename Polynomial::value_type coeff_t;
bool plus=false, not_one;
if ( degree(p)<0)
os << coeff_t(0) ;
else {
for(int i= 0; i<=degree(p); i++)
{
if(p[i]!= (coeff_t)0)
{
not_one = (p[i] != (coeff_t)1);
if(not_one || i==0)
print_as_coeff(os,p[i],plus);
plus=true;
// if(i != degree(p) && with_plus_sign(p[i])) os<<"+";
if(i>0)
{
// if(p[i] == (coeff_t)(-1)) os<<"-";
// else
if(not_one)
os<<"*";
os<<"x";
if(i !=1)
{os<<'^'; os<<i;}
}
// else
// os<<p[0];
}
}
if(!plus) os << 0 ;
}
return os;
}
| OSTREAM& mmx::univariate::print | ( | OSTREAM & | os, |
| const monomials< C > & | p | ||
| ) | [inline] |
| OSTREAM& mmx::univariate::print_as_coeff | ( | OSTREAM & | os, |
| const C & | c, | ||
| bool | plus | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 367 of file univariate.hpp.
Referenced by print().
{
if(plus)
os <<"+";
os<<"("<<c<<")";
return os;
}
| void reciprocal | ( | R & | w, |
| const R & | p | ||
| ) |
Compute the reciprocal of the univariate polynomial 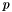 . The result is given in
. The result is given in 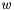 . We assume
. We assume ![$p[0] != 0$](form_4.png) . For this, we consider the equation
. For this, we consider the equation  , where
, where 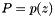 ,
, 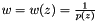 over the ring of formal power series in
over the ring of formal power series in  , and apply Newton's iteration to this equation. So we have :
, and apply Newton's iteration to this equation. So we have : 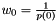 , and
, and 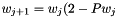 where
where 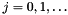 By reducing the different polynomials modulo
By reducing the different polynomials modulo 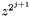 at each step, we have two convolutions of two pairs of vectors of dimensions at most
at each step, we have two convolutions of two pairs of vectors of dimensions at most 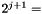 by step.
by step.
Definition at line 660 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree(), mmx::log(), mmx::pow(), and reduce().
{
typedef typename R::size_type size_type;
typedef typename R::value_type C;
const size_type deg = univariate::degree(p)+1;
R w0(deg),v(deg),xp(p);
size_type K = (size_type) (std::log(p.degree()+1)/std::log(2)),j=1;
C p0 = xp[deg-1];
xp /= p0;
w0 =xp/xp[0];
v = w0;
v *= C(-1.0);
v[0]+=C(2);
w=v/xp[0];
w0=w;
while (j <= K) {
univariate::reduce(w0,pow(2,j+1));
w=xp*w0;
v =w;
v*=C(-1.0);
v[0]+=C(2);
univariate::reduce(v,pow(2,j+1));
w=w0*v;
w0=w;
j++;
}
univariate::reduce(w,deg);
w/=p0;
}
| void mmx::univariate::reduce | ( | T & | p, |
| const typename T::size_type & | e | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Truncate an univariate polynomial 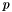 which is modified in output, with a new degree of
which is modified in output, with a new degree of 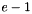 .
.
Definition at line 696 of file univariate.hpp.
{
// il me semble que tout ca c'est la meme chose que p.resize(e)
T temp(e);
for (typename T::size_type i = 0; i < e; i++) temp[i]=p[i];
p.resize(e);
// p.degree()=e-1;
for (typename T::size_type i = 0; i < e; i++) p[i]=temp[i];
}
| void mmx::univariate::reduce | ( | R & | p, |
| const typename R::size_type & | e | ||
| ) |
Referenced by reciprocal(), and subdivisor< CELL, V >::run().
| void mmx::univariate::reverse | ( | R & | p, |
| typename R::size_type | n | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 590 of file univariate.hpp.
References mmx::sparse::swap().
Referenced by mmx::min_bound().
{
int l=n-1;
for(typename R::size_type i=0;i<n/2;i++)
std::swap(p[i],p[l-i]);
}
| void mmx::univariate::reverse | ( | T & | p, |
| int | n | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Reverse the coefficients of an univariate polynomial, it is performed in place. For a call of this function, the list of arguments must specify, in last, an instance of univariate, the generic type 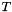 is assumed to be a valid class of univariate polynomial. Example of such a call:
is assumed to be a valid class of univariate polynomial. Example of such a call:
upoldse<...> p(...); univariate::reverse(p,i);
Definition at line 716 of file univariate.hpp.
References mmx::sparse::swap().
{ for ( int i = 0; i < n/2; i++ ) std::swap(p[i],p[n-i]) ; }
| void scale | ( | R & | r, |
| const R & | p, | ||
| const C & | l | ||
| ) |
Scale the variable in the polynomial p by l and put the result r. It computes the coefficients of the polynomial 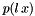 .
.
Definition at line 812 of file univariate.hpp.
Referenced by convertm2b(), and mmx::scale().
{
r=p;
C s(l);
for(unsigned i=1; i< p.size();i++){
r[i]*=s;
s *=l;
}
}
| void mmx::univariate::set_monomial | ( | R & | x, |
| const C & | c, | ||
| unsigned | n | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 418 of file univariate.hpp.
References checkdegree(), and mmx::array::set_cst().
{
x.resize(n+1);
array::set_cst(x,(typename R::value_type)0);
x[n]=c;
checkdegree(x);
}
| void mmx::univariate::shift | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | p, | ||
| int | d, | ||
| int | v = 0 |
||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 318 of file univariate.hpp.
References degree().
Referenced by convertm2b(), shift(), and mmx::shift().
| void mmx::univariate::shift | ( | R & | r, |
| const R & | p, | ||
| const C & | x0 | ||
| ) |
Shift the polynomial p at the point x0 and put the result in r. In other words, it computes the coefficients of the polynomial 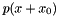 .
.
Definition at line 790 of file univariate.hpp.
References shift().
{
r=p; shift(r,x0);
}
| void mmx::univariate::shift | ( | R & | p, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) |
Inplace shift of the polynomial r at the point x0. It computes the coefficients of the polynomial 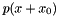 .
.
Definition at line 778 of file univariate.hpp.
{
int j,k,s;
for ( s = p.size(), j = 0; j <= s-2; j++ )
for( k = s-2; k >= j; p[k] += c*p[k+1], k-- ) ;
};
| int mmx::univariate::sign_at | ( | const POL & | p, |
| const X & | x | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 547 of file univariate.hpp.
References eval_horner(), and mmx::sign().
{
X v= eval_horner(p,x);
return sign(v);
}
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | ||
| const monomials< C > & | b | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 250 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree().
Referenced by div_rem(), use< operators_of, univariate::monomials< C > >::sub(), and sub().
{
array::sub(r,a,b);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | ||
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 262 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
{
if(degree(a)>-1) {
r=a; r[0]-=c;
}
else
r= Polynomial(-c,0);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | ||
| const X & | x | ||
| ) | [inline] |
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const C & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 277 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
{
if(degree(r)>-1) {
r[0]-=c;
}
else
r= Polynomial(-c,0);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, |
| const monomials< C > & | a | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 256 of file univariate.hpp.
References check_degree(), and sub().
{
array::sub(r,a);
check_degree(r);
}
| void mmx::univariate::sub_cst | ( | R & | r, |
| const S & | c | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 432 of file univariate.hpp.
{ r[0]-=c;}
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::tcoeff | ( | const R & | p | ) | [inline] |
Return the tail coefficient of the polynomial p.
Definition at line 363 of file univariate.hpp.
{ return p[0]; }