


Next: Image import
Up: manual
Previous: Tensor flipping
Contents
Registration Tool Module
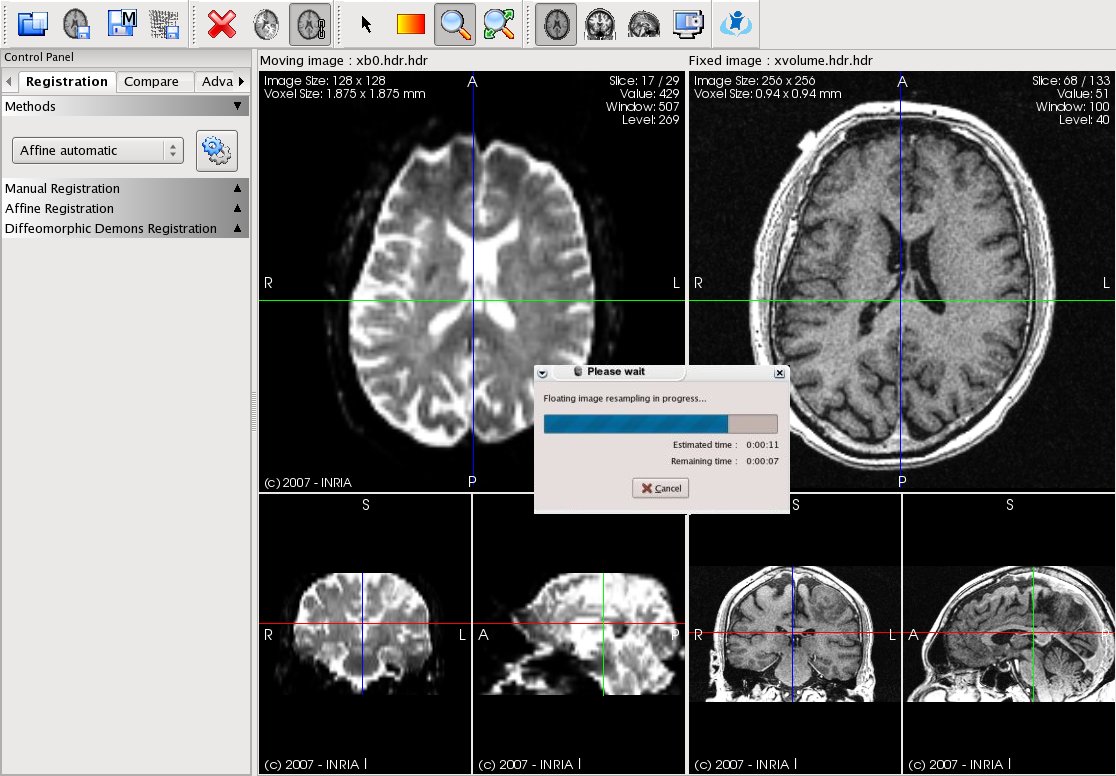
Figure:
The RegistrationTool main window. shown here during the rigid
registration process between different MR modalities of a single patient.
|
|
RegistrationTool is dedicated to image registration. Among all image processing algorithms, registration remains a common yet challenging pre-processing step before doing statistical analysis, group comparisons or atlas formation. This application provides a simple interface for several kinds of registration. It takes two images as input, the ``fixed image'' and the ``moving image'', and offers up to now three ways of registering them:
- Manual Rigid Registration: In a few clicks, one can perform a manual rigid registration of two images. Rigid registration consists in a translation and a rotation. This is done very simply by asking the user to place in both fixed and moving images a point plus a direction. The two points are used to compute the translation, and the directions are used to calculate the angle of rotation. See Sec. 5.3 for more details.
- Automatic Affine Registration: We use the affine registration framework of ITK [#!ITKSoftwareGuide!#] to achieve this automatic matching of images. It consists in maximizing the mutual information of the two images, and is embedded in a multi-resolution framework.
No user input is required. This method gives optimal results when registering two images of the same patient acquired at different times. For matching images of different subjects, one should rely on the last method. See Sec. 5.4 for more details.
- Automatic Diffeomorphic Demons Registration: This method provides a very up-to-date method for non-linear registration [#!Vercauteren:ISBI:2006!#]. This procedure is based on variants of the Thirion's demons algorithm [#!Thirion:MIA:1998!#] for non-linear mono-modal image registration.
It is fast, and insures the invertibility of the transform, which is a very desirable feature in registration. See Sec. 5.5 for more details.

 The user simply has to choose his desired registration method - possibly set some parameters - and press the ``Perform'' button. For user convenience a ``Reset'' button allows the user to cancel all previous registration and go back to the initial state.
The user simply has to choose his desired registration method - possibly set some parameters - and press the ``Perform'' button. For user convenience a ``Reset'' button allows the user to cancel all previous registration and go back to the initial state.
One of the most challenging goals in this type of tool is to provide an intuitive way of performing registration as well as an easy manner in the evaluation of the results' accuracy. In RegistrationTool an effort has been made in this direction. As shown in Fig. 5.1 the user interface integrates separated tabs for each of the input images. Each tab can be divided once more in three showing respectivelly the axial, the coronal and the sagittal view of the 3D volumic image, following the radiological conventions. Fixed and moving images can be synchronized one to the other to evaluate their degree of geometry difference. A full screen mode allows to have a complete freedom in terms of visualization.
Subsections



Next: Image import
Up: manual
Previous: Tensor flipping
Contents
Nicolas Toussaint
2007-06-22

![]()
![]() The user simply has to choose his desired registration method - possibly set some parameters - and press the ``Perform'' button. For user convenience a ``Reset'' button allows the user to cancel all previous registration and go back to the initial state.
The user simply has to choose his desired registration method - possibly set some parameters - and press the ``Perform'' button. For user convenience a ``Reset'' button allows the user to cancel all previous registration and go back to the initial state.