- AOL-cosh1
- Non algebraic: AOL-legentil
- AOL-log1
- Box3
- Branin system
- Bratu
- Bullard
- Collins
- comp.soft-sys.math.maple-14706
- Design problem
- DiGregorio
- Electrical circuit
- Extended Powell
- Ferraris
- Gaussian
- Geometrica1
- Helical
- Helical1
- Helical valley
- Jennrich1
- Kincox modified
- Kin1 modified
- Lambert
- Lambert1
- Mixed algebraic-trigonometric
- Powell
- Puma modified
- Reactor
- Rump univariate
- sci.math.num-analysis1
- sci.math.num-analysis-89741
- sci.math.num-analysis90897
- sci.math.num-analysis92191
- sci.math.num-analysis97384
- Semi-conductor (Molenaar)
- Sinxx
- Sinxx1
- Sjirk-Boon
- stoutemyer-eq-2007
- Trigexp1
- Trigexp2
- Trigexp3
- Trigo1
- Troesch
- Xu
- Zufiris
Non-polynomial systems
AOL-cosh1
Origin:AOL
3 equations
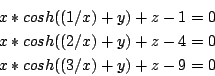
Ranges: [-100,100]
Solving method: GradientSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (October 2004):
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 5.96s |
Non algebraic: AOL-legentil
3 equations10/3*cos(x)/sin(x)^2+4*(1+tan(x)^2)/cos(y)+z*(-50/3*sin(y)*cos(x)/(sin(x)^2*(3.5-5*sin(y)))-10/3*cos(x)/sin(x)^2-4*(1+tan(x)^2)/cos(y))=0 4*tan(x)*sin(y)/cos(y)^2+z*(50/3*cos(y)/(sin(x)*(3.5-5*sin(y)))+250/3*sin(y)*cos(y)/(sin(x)*(3.5-5*sin(y))^2)-4*tan(x)*sin(y)/cos(y)^2)=0 50/3*sin(y)/(sin(x)*(3.5-5*sin(y)))+20+10/3/sin(x)-4*tan(x)/cos(y)=0Ranges:
Solving method: GradientSolve+3B+Simp2B
Solutions:: 0
Computation time:
| DELL D620 (1.7GHz), (May 2007): | 9mn |
AOL-log1
Origin:AOL
Range: [1,1000]
Solving method: GradientSolve
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (February 2005):
| Sun Blade | 0.06s |
Box3
Origin: [9]Let
and
for i =1,2,3
Range: [-100,100],[-100,100],[0.1,100]
Solving method: HessianSolve,3B,2B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| EVO 410C (1.2GHz) | 10.4s |
Branin system
Origin: mentioned by Rump[11]
Ranges: for all unknowns [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: GradientSolve,3B,HullConsistency
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (September 2006):
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.01s |
Bratu
Physical meaning: PDE in combustion theoryOrigin: unknown
Let
and
with n=15 Unknowns: x,.., xn
Range: [-1e8,20]
Solving method: HessianSolve,HullConsistency
Solutions:: 2 pour n=15, 30 (exact)
Computation time:
| Sun Blade | 6.94s (April 2003) |
| DELL D400 (1.7Ghz) | 0.59s (n=15), 9.1s (n=30 (May 2004)) |
Bullard
Origin: [6]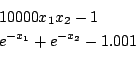
Ranges: [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 0.01s |
Collins
Origin: [2]
Physical meaning: allows to determine the configuration of a
parallel robot being given its joint coordinates
Range: [-1,1]
Solving method: GradientSolve,HullConsistency
Solutions:: 6 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| EVO 410C (1.2GHz) | 0.2s |
comp.soft-sys.math.maple-14706
Origin: Article 14706 of comp.soft-sys.math.maple
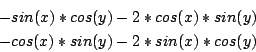
Ranges: [0,2Pi]
Solving method: HessianSolve+3B
Solutions:: 13 (exact)
Computation time (November 2005):
| Sun Blade | 11.36s |
Design problem
Origin: [6]
9 equations

23.3037 x_2+(1-x_1 x_2)x_3 (e^{x_5 ( 0.485- 0.0052095 x_7- 0.0285132 x_8)}-1)- 28.5132
- 28.5132 x_1+(1-x_1 x_2)x_4 (e^{x_6 ( 0.116- 0.0052095 x_7+ 0.0233037 x_9)}-1)+ 23.3037
101.779 x_2+(1-x_1 x_2)x_3 (e^{x_5 ( 0.752- 0.0100677 x_7- 0.1118467 x_8)}-1)- 111.8467
- 111.8467 x_1+(1-x_1 x_2)x_4 (e^{x_6 (- 0.502- 0.0100677 x_7+ 0.101779 x_9)}-1)+ 101.779
111.461 x_2+(1-x_1 x_2)x_3 (e^{x_5 ( 0.869- 0.0229274 x_7- 0.1343884 x_8)}-1)- 134.3884
- 134.3884 x_1+(1-x_1 x_2)x_4 (e^{x_6 ( 0.166- 0.0229274 x_7+ 0.111461 x_9)}-1)+ 111.461
191.267 x_2+(1-x_1 x_2)x_3 (e^{x_5 ( 0.982- 0.0202153 x_7-0.2114823 x_8)}-1)- 211.4823
- 211.4823 x_1+(1-x_1 x_2)x_4 (e^{x_6 (- 0.473- 0.0202153 x_7+ 0.191267 x_9)}-1)+ 191.267
x_1 x_3-x_2 x_4
Ranges: [0,10]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistencyStrong
+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time:
| Cluster (11 PC's) | 3h 49mn (April 2003) |
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 398s (May 2004) |
DiGregorio
Origin:Digregorio [3]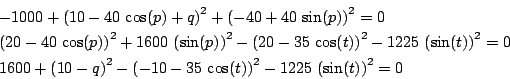
Ranges: for
Solving method: GradientSolve+3B
Solutions:: 4 (exact)
Computation time (September 2006):
| DELL D400 (1.7Ghz) | 0.55s |
Electrical circuit
Origin:Quateroni A, Sacco, R. and Saleri, F., Numerical mathematics, Springer 2000, pp. 413
Solve in ![]() :
:
with
Ranges: [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistencyStrong
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time:
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.003s (February 2006) |
Extended Powell
Origin: [8]
n=2m equations:
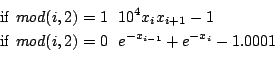
Ranges: [-100,100]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistencyStrong+3B
Solutions:: 32 (n=10), 200 (n=20) (exact)
Computation time:
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 23.32s (n=10) (April 2003) |
| DELL D400 (1.7Ghz) | 1.72s (n=10), 88.48s (n=20) (May 2004) |
Ferraris
Origin: [6]
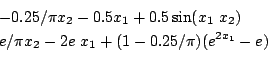
-0.25/Pi*x2 - 0.5*x1 + 0.5*sin(x1*x2); exp(1)/Pi*x2 - 2*exp(1)*x1 + (1 - 0.25/Pi)*(exp(2*x1) -exp(1));Ranges: [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 12 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 0.16s |
Gaussian
Origin:COPRIN, derived from [9]
3 equations:
with
Ranges: [-9,9] for all unknowns
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistencyStrong+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time:
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 12.84s (April 2003) |
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 2.33s (May 2004) |
Geometrica1
Origin:COPRIN, derived from a mesh problem submitted by
M. Pouget and F. Cazals from the Geometrica project.
2 equations, 2 unknowns:
(36/25+(x+1)^2)^(1/2)+1/2*(36/25+(1+y)^2)^(1/2)+1/2*(72/25+(-x+1+y)^2)^(1/2)+ (36/25+(1-x)^2)^(1/2)+1/2*(36/25+(2-y)^2)^(1/2)+ 1/2*(72/25+(x+2-y)^2)^(1/2)-4*2^(1/2)-3^(1/2)=0 signum(-1/(36/25+(1+y)^2)^(1/2))*arccos((1+y)/(36/25+(1+y)^2)^(1/2))+Pi+ 2*signum(-1/(36/25+(1-x)^2)^(1/2))*arccos((1-x)/(36/25+(1-x)^2)^(1/2))+ 2^(1/2)*signum(-1/(72/25+(x+2-y)^2)^(1/2))* arccos((x+2-y)/(72/25+(x+2-y)^2)^(1/2))+ signum(-1/(36/25+(2-y)^2)^(1/2))*arccos((2-y)/(36/25+(2-y)^2)^(1/2))+ ((x-1)^2+y^2+36/25)^(1/2)* signum((366+150*y^2+150*x^2-300*x)/(72/25+(-x+1+y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(1-x)^2)^(1/2))* arccos(1/25*(61+25*x^2-50*x-25*x*y+25*y)/(72/25+(-x+1+y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(1-x)^2)^(1/2))+ 2*signum(-1/(36/25+(x+1)^2)^(1/2))* arccos((x+1)/(36/25+(x+1)^2)^(1/2))+(x^2+(y-2)^2+36/25)^(1/2)* signum((816+150*y^2-600*y+150*x^2)/(72/25+(x+2-y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(2-y)^2)^(1/2))* arccos(1/25*(136-25*x*y-100*y+25*y^2+50*x)/(72/25+(x+2-y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(2-y)^2)^(1/2))+ (x^2+(1+y)^2+36/25)^(1/2)* signum((366+300*y+150*y^2+150*x^2)/(72/25+(-x+1+y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(1+y)^2)^(1/2))* arccos(1/25*(61-25*x+50*y-25*x*y+25*y^2)/(72/25+(-x+1+y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(1+y)^2)^(1/2))+ ((x+1)^2+(y-1)^2+36/25)^(1/2)* signum((300*x-300*y+516+150*y^2+150*x^2)/(72/25+(x+2-y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(x+1)^2)^(1/2))* arccos(1/25*(86+25*x^2+75*x-25*x*y-25*y)/(72/25+(x+2-y)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(x+1)^ 2)^(1/2)) -4*2^(1/2)*arccos(1/3*3^(1/2)*2^(1/2))+2^(1/2)* signum(-1/(72/25+(-x+1+y)^2)^(1/2))* arccos((-x+1+y)/(72/25+(-x+1+y)^2)^(1/2))+((x-1)^2+(y-2)^2+36/25)^(1/2)* signum((966+150*y^2-600*y+150*x^2-300*x)/(36/25+(1-x)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(2-y)^2)^(1/2))* arccos((x-1)*(y-2)/(36/25+(1-x)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(2-y)^2)^(1/2))+((x+1)^2+(1+y)^2+36/25)^(1/2)* signum((516+300*y+150*y^2+150*x^2+300*x)/(36/25+(x+1)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(1+y)^2)^(1/2))* arccos((x+1)*(1+y)/(36/25+(x+1)^2)^(1/2)/(36/25+(1+y)^2)^(1/2))+ 2*2^(1/2)*arccos(1/3*3^(1/2))-2/3*3^(1/2)*Pi =0where signum(x)=1 if
Ranges: [-1,1] for all unknowns
Solving method: GeneralSolve
Solutions:: 0 (exact)
Computation time:
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 1.7s (July 2004) |
Helical
Origin: [9]
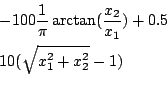
Range: x1 in [-1e8,-1e-3], x2 in [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: GradientSolve,3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| EVO 410C (1.2GHz) | 0.04s |
Helical1
Origin: COPRIN, derived from [9]
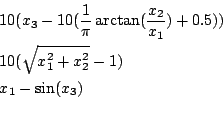
Range: x1 in [-1e8,-1e-3], x2,x3 in [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: GradientSolve,3B
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| EVO 410C (1.2GHz) | 0.08s |
Helical valley
Origin:
Range: x1 in [-1e8,1e8], x2 in [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: GradientSolve,3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| DELL D620 (1.7GHz) | 0.02s |
Jennrich1
Origin: COPRIN, derived from [9]
2 equations with 2 unknowns
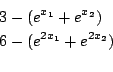
Range: [-5,5] for all unknowns
Solving method: HessianSolve,3B
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| EVO 410C (1.2GHz) | 0.01s |
Kincox modified
Origin: COPRIN, derived from Kincox COCONUT
2 equations with 2 unknowns with a =1, b=4, l1=10, l2=6
-1.+6.*cos(t1)*cos(t2)-6.*sin(t1)*sin(t2)+10.*cos(t1)=0 -4.+6.*cos(t1)*sin(t2)+6.*cos(t2)*sin(t1)+10.*sin(t1)=0Ranges: [0,2
Solving method: GradientSolve+HullConsistencyStrong+
+3B
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (May 2004):
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.04s |
Kin1 modified
Origin: COPRIN, modified from COCONUT kin1
sin(t2)*cos(t5)*sin(t6)-sin(t3)*cos(t5)*sin(t6)-sin(t4)*cos(t5)*sin(t6)+ cos(t2)*cos(t6)+cos(t3)*cos(t6)+cos(t4)*cos(t6)-0.4077 =0 cos(t1)*cos(t2)*sin(t5)+cos(t1)*cos(t3)*sin(t5)+cos(t1)*cos(t4)*sin(t5) +sin(t1)*cos(t5)-1.9115 =0 sin(t2)*sin(t5)+sin(t3)*sin(t5)+sin(t4)*sin(t5)-1.9791 =0 cos(t1)*cos(t2)+cos(t1)*cos(t3)+cos(t1)*cos(t4)+cos(t1)*cos(t2)+ cos(t1)*cos(t3)+cos(t1)*cos(t2)-4.0616 =0 sin(t1)*cos(t2)+sin(t1)*cos(t3)+sin(t1)*cos(t4)+sin(t1)*cos(t2)+sin(t1)*cos(t3)+sin(t1)*cos(t2)-1.7172 =0 sin(t2)+sin(t3)+sin(t4)+sin(t2)+sin(t3)+sin(t2)-3.9701 =0Ranges: [0,
Solving method: HessianSolve+3B+HullConsistencyStrong
Solutions:: 16 (exact)
Computation time:
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 155.18s (August 2004) |
Lambert
Origin: a classical astronomy problem
We define:
r0,r;
11 10
.138256930224638 10 , .68876844473745 10
mu:=13.271244e10:
dnu:=Pi/4.:
A:=sqrt(r0*r*(1+cos(dnu))):
S:=(u-sin(u))/u^3:
y:=r0+r-A*sin(u)/sqrt(1-cos(u)):
x:=u*sqrt(y)/sqrt(1-cos(u)):
The equation to solve in Ranges: [0.1, 2
Solving method: GradientSolve+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time:
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.11s (September 2006) |
Lambert1
Origin: another formulation of a classical astronomy problem
We define:
r0,r;
11 10
.138256930224638 10 , .68876844473745 10
mu:=13.271244e10:
We then define
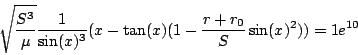
Ranges: [0.1,
Solving method: GradientSolve+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time:
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.04s (September 2006) |
Mixed algebraic-trigonometric
Origin:sci.math.num-analysis
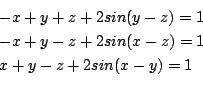
Ranges: [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time:
| Sun Blade | 6.85s (April 2003) |
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.1s (May 2004) |
Powell
Origin: [9]
Ranges: [-100,100] for all unknowns
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 0.01s |
Puma modified
Origin: COPRIN, modified from COCONUT Puma
Physical meaning: inverse kinematics of a 3R robot, the angles
t1,t2,t3 are the angles of the three joints
4 equations with 4 unknowns
.4731e-2*cos(t1)*cos(t2)-.3578*sin(t1)*cos(t2)-.1238*cos(t1) -.1637e-2*sin(t1)-.9338*sin(t2)+cos(t4)-.3571=0 .2238*cos(t1)*cos(t2)+.7623*sin(t1)*cos(t2)+.2638*cos(t1) -.7745e-1*sin(t1)-.6734*sin(t2)-.6022=0 sin(t3)*sin(t4)+.3578*cos(t1)+.4731e-2*sin(t1)=0 -.7623*cos(t1)+.2238*sin(t1)+.3461=0Ranges: [0,
Solving method: GradientSolve+HullConsistencyStrong+
+3B
Solutions:: 16 (exact)
Computation time (May 2004):
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.48s |
Reactor
Origin: [6]
Ranges: [100,1000]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 3 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 0.06s |
Rump univariate
Origin: mentioned by Rump[11]Ranges: [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: HessianSolve,3B
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (September 2006):
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.006s |
sci.math.num-analysis1
Origin: Article 86825 of sci.math.num-analysis
Ranges: [-100,100]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 65 (49 approximate, 16 exact)
Computation time (September 2005):
| DELL D400 (1.2Ghz) | 0.06s |
Solutions:: 65 (1 approximate, 64 exact)
Computation time (November 2005):
| DELL D400 (1.2Ghz) | 1069s |
sci.math.num-analysis-89741
Origin: Article 89741 of sci.math.num-analysis
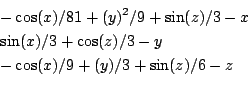
Ranges: [-1e8,1e8] for all unknowns (may be largely improved..)
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 1, exact
Computation time (April 2006):
| DELL D400 (1.2Ghz) |
sci.math.num-analysis90897
Origin: Article 90897 of sci.math.num-analysis
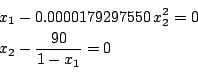
Ranges: [-1000,0.99],[-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: HessianSolve+3B
Solutions:: 2 (exact)
Computation time (June 2006):
| Sun Blade | 0.13s |
sci.math.num-analysis92191
Origin: Article 92191 of sci.math.num-analysis
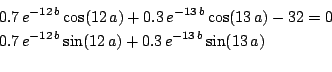
Ranges: [0,![]() ],[-10,30]
],[-10,30]
Solving method: HessianSolve or GradientSolve+3B
Solutions:: 14 (exact)
Computation time (September 2006):
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 21.3s (GradientSolve), 68.15s (HessianSolve) |
sci.math.num-analysis97384
Origin: Article 97384 of sci.math.num-analysis
Modified by COPRIN to scale the unknown
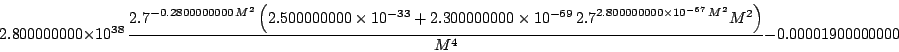
Ranges: [1e-4,1000]
Solving method: HessianSolve+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (July 2007):
| DELL D620 (1.7Ghz) | 0.01s |
Semi-conductor (Molenaar)
Origin: J. Molenaar, P.W. Hemker:
A multigrid approach for the solution of the
2D semiconductor equations.
IMPACT Comput. Sci. Eng. 2, No. 3, p. 219-243 (1990).
6 equations with a=38.683, ni=1.22e10, V=100, DDD=10.e17.
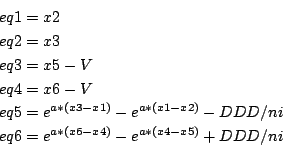
Ranges: [-400,400]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Sun Blade | 0.16s |
Sinxx
Origin: COPRIN
Range: [0,A], where A may be chosen arbitrary large without any change in the computation time
Solving method: GradientSolve,HullConsistency
Solutions:: 32 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Sun Blade | 0.051s |
Sinxx1
Origin: COPRIN
Range: [-10,10]
Solving method: GradientSolve,HullConsistency
Solutions:: 9 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Sun Blade | 0.062s |
Sjirk-Boon
Origin: news from Sjirk-Boon, modified by COPRIN
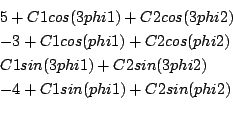
Range: [-100,100] for ![]() ,
, ![]() for
for ![]()
Solving method: GradientSolve,Simp2B, 3B
Solutions:: 8 (exact)
Computation time:
| Dell D620 (1.7GHz) (May 2007) | 94s |
stoutemyer-eq-2007
Origin: [12]
Range: [-1e8,1e8]
Solving method: GradientSolve
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time (November 2007):
| DELL D620 | 0.01s |
Trigexp1
Origin: [8]
n equations:
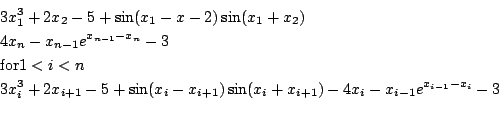
for n=20
Ranges: [-100,100]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistencyStrong+3B
Solutions:: 1 (exact) for n=20,30, 50
Computation time:
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 693.88s (April 2003) |
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.9s (n=20), 2.3s (n=30) 12.9s (n=50) (May 2004) |
Trigexp2
Origin: [8]
n=2m+1 equations:
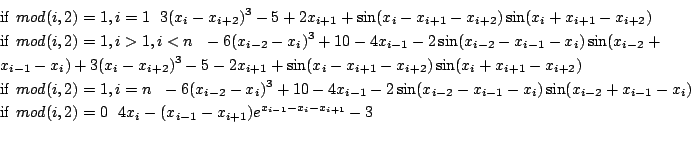
Ranges: [-200,200]
Solving method: HessianSolve or GradientSolve +HullConsistencyStrong+
3B
Solutions:: 0 (n=5,7,9,11) (exact)
Computation time (May 2004):
| DELL D400 (1.7Ghz) | 15.31s (n=5) 58.59s (n=7) 115.3s (n=9) 327s (n=11) |
Solutions:: 0 (n=21) (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 2202s |
Trigexp3
Origin: [8]
n equations with h=1/(n+1):
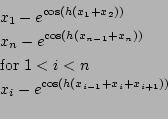
for n=20,40
Ranges: [
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 1 for n=20, 40 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Evo 410C (1.2Ghz) | 0.51s (n=20), 2.64s (n=40) |
Trigo1
Origin: [9]
n equations:
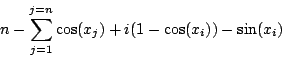
for n=5
Ranges: [0.1,
Solving method: HessianSolve+3B+HullConsistencyStrong
Solutions:: 1 (exact)
Computation time:
| Evo 410C (1.2GHz) | 1.09s (April 2003) |
| DELL D400 (1.7GHz) | 0.36s (May 2004) |
Troesch
Origin: [8]
n equations with h=1/(n+1),R =10:
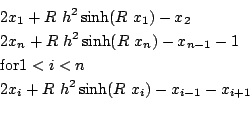
for n=10,20
Ranges: [-10,10]
Solving method: HessianSolve+HullConsistency+3B
Solutions:: 1 for n=10, 15 (exact)
Computation time (April 2003):
| Evo 410C (1.2GHz) | 32.83s (n=10), 407s (n=15) |
Xu
Origin: [14]
2 equations
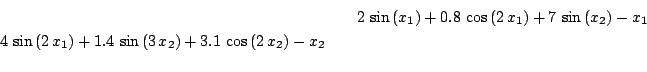
Ranges: [-20,20] for
Solving method: GradientSolve+Simp2B+3B
Solutions:: 29 (exact)
Computation time:
| DELL D620 (1.7GHz), (July 2007) | 0.037s |
Zufiris
Origin: [16]
4 equations

Ranges: [
Solving method: HessianSolve+Simp2B+3B
Solutions:: 13 (exact)
Computation time:
| DELL D620 (1.7GHz), (July 2007) | 0.07s |