



Next: How to save an
Up: How to run the
Previous: How to visualize isovalues
Contents
Index
- If you set the toggle ``Show colmap'' in the
working window, a new window is added to the main drawing window for the
visualization of the current colormap.
- For differents colormaps are provided in the menu
``colormap'' of the working window. Choose a
different one, then ``redraw''.
- To modify the number of colors of this
colormap, set the toggle ``Set Isos'', a window appears
(figure 1.14) in which you can
set a number in ``nb colors''. Press the button ``adjust'' to show the colormap
with the new number of colors. Similiarly you can change the number of lines
and press ``adjust'' for an automatic computation of isolines values between
the minimun and the maximun values of the current variable.
Figure 1.14:
Set scales of the colormap.
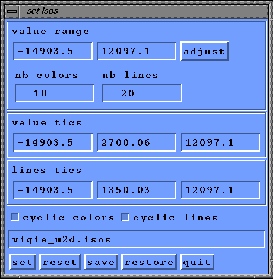 |
- In the first frame of the ``setIsos'' window, under the label
``value range'', the extremun values of the current variables are displayed
in editable windows. The default values are just under the minimun of the
current variable for all the solutions of the current problem, and above
the maximun. To show the exact extremun, you can set the ``global extr.''
toggle on, push the ``redraw'' button and look at the drawing window of
the colormap. The default values differ from the exact extremun to avoid
drawing an isoline in an area where the value in each node is exactly the
iso value. You can modify the value range and press adjust.
- In the next frame of the ``setIsos'' window, you can modify the
``value tics''; theses values are used
to represent the color areas. The first value is the minimun, the second
is the increment between each value, and the last define the maximun. You
can change one or more of theses values and press the ``set'' pushbutton
at the left bottom of the ``setIsos'' window to set the new color areas.
- The next frame of the ``setIsos'' window allows to modify the
``lines tics''; theses values are used
to define the isovalue lines. The first value is the value of the first
isoline, the second is the increment between each isoline, and the last
define the value of the last isoline. You
can change one or more of theses values and press the ``set'' pushbutton
at the left bottom of the ``setIsos'' window to show the new isovalues
in the ``colmap'' window.
- You can choose a ``cyclic color'' .
If this toggle button is off: above the maximum of the values
(defined in the ``value tics'') and under the minimum of the values, the
maximum (minimum) color is drawn.
Otherwise if this toggle button is on:
above the maximum of the values and under the minimum, colors are
drawn in cyclical mode.
- You can choose a ``cyclic lines''
(figure 1.14). If this toggle button is off: above the maximum
of the lines (defined in the ``lines tics'') and under the minimum,
lines are not drawn.
Otherwise if this toggle button is on, they
are drawn above the maximum of the lines (under the minimum).
- If you want to save these value and lines ranges, name the file
(default name: vigie_2d.isos) and push the ``save'' button.
Then ``restore'' allows to restore the
value and lines ranges saved in the named file.
- To go back to the initial ranges and tics, push the ``reset'' button
at the bottom of the ``setisos'' window
(figure 1.14).
- You can leave the ``set Isos'' mode by pushing the ``quit'' button
at the bottom of the ``setisos'' window, or by resetting the toggle
``Set Isos'' in the working window.




Next: How to save an
Up: How to run the
Previous: How to visualize isovalues
Contents
Index
Robert Fournier
2002-09-13
