| R macaulay | ( | const L & | f, | |
| unsigned int | nu, | |||
| unsigned int | nv, | |||
| char | z = 'T' | |||
| ) |
Construction of the matrix of all multiples of degree nu of all the polynomials f[0], f[1], , f[n]. The argument nv is the number of variables. The order choosed to sort the monomials indexing the rows of the matrix is the {reverse} order associated to the polynomials of the sequence f. The second template argument specifies the type of the output matrix. For instance, macaulay<Mat>(f); will output a Mat. The usual Macaulay matrix is a submatrix of this one, for 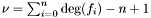 .
.
Definition at line 223 of file macaulay.h.
References matrixof::assigncoeff(), and matrixof::reserve().
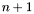 polynomials in n variables. It will be of minimal degree in the coefficients of
polynomials in n variables. It will be of minimal degree in the coefficients of  ,
,  matrix and the method
matrix and the method 