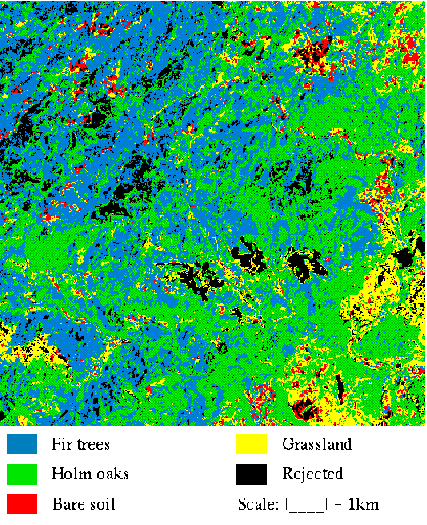

The pixel is labelled with his dominating label . There are as many classes as reference spectra.
The comparison with the vegetation map shows that the mixing percentages classification is closer to the ground than the maximum likelihood one. This is due to the fact that the spectral domains of the holm oaks and the fir trees are very close.
Whereas the maximum likelihood classification enables us to deal with those close spectra, our method permits us to separate them.
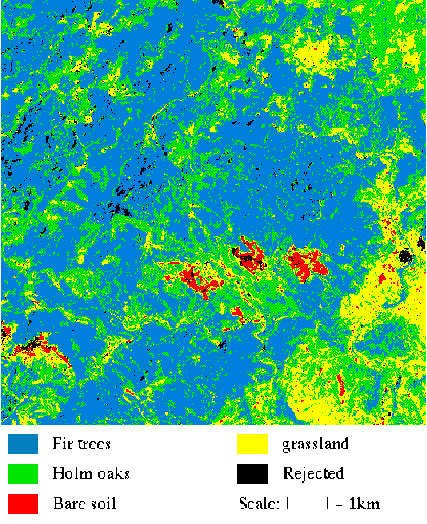
One can see another example of classification.