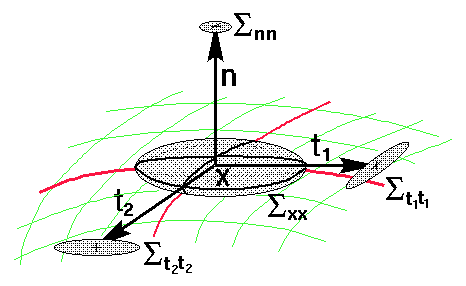
Using a compositive model of noise on frames amounts to express the error in the local frame:

Estimated noise on extremal points considered as frames.
The standard deviation for the position in the tangent plane is roughtly 0.5mm versus 0.25mm only along the normal.
The standard deviation of the normal is about 3 deg in both directions whereas it is about 12 deg for the principal directions in the tangent plane.
If we forget the thihedron, the estimation of an additive noise on extremal points gives an isotropic noise of standard deviation 0.5 mm. The compositive noise model on frames captures thus much more information.
With this model of noise, and using
a ![]() value of
16 for frames and 8 for points, we obtain a selectivity (basic probability
of false match for one feature) of:
value of
16 for frames and 8 for points, we obtain a selectivity (basic probability
of false match for one feature) of:
|
|
|
With these values, we have estimated the probability of finding n matches n two random "images" of 2500 extremal points.
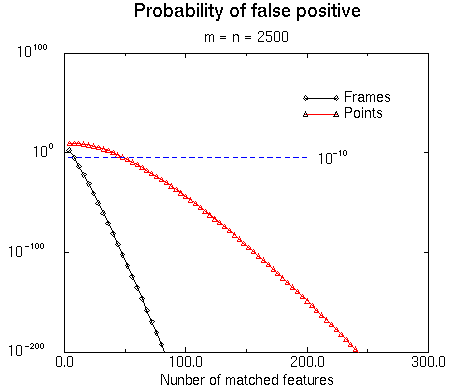
The probability of obtaining around 500 matches (mean number of matches for our registrations) is indeed negligible for points as for frames, but it is interesting to note that we need roughtly 5 times more point matches than frame matches to obtain the same probability (10 frames and 56 point matches for a probability of 1e-10).