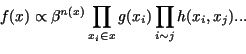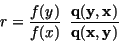

Next: Road network extraction
Up: Roads Extraction using a
Previous: Roads Extraction using a
Probabilistic methods in image processing
- Bayesian framework, Markov Random Fields
- Random variables: pixels
- Local interaction
- Correlated noise ?
- No geometric constraints
Markov Object Processes
Notations :
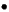
- Image space: T
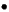
- Object space: U (object parameters)
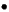
- Objet support: R(u)
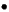
- Configuration:
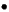
- Configurations space:
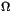
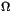 is a measurable space, with measure
is a measurable space, with measure 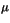 ,
corresponding
to a uniform Poisson process.
,
corresponding
to a uniform Poisson process.
Poisson process :
n(x) = number of objects of the configuration x.
Markov Object Process :
Markov Object Process simulation
Simulation using a Markov Chain : find a Markov chain Xt such that
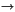 MCMC methods
MCMC methods
RJMCMC algorithm
Description:
- general scheme
- every transition can be defined: at each step,
a transition from the current state x to a new state y is proposed
- the transition is accepted with a probability
depending on an acceptance ratio which depends on the law f
- Challenge: define ``good'' transitions
We consider a proposal density q(.,.) which can be easily simulated.
At step t, Xt=x :
- 1.
- simulate y with density q(.,.)
- 2.
- compute:
- 3.
- with probability
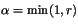 ,
set Xt+1=y, otherwise Xt+1=x
,
set Xt+1=y, otherwise Xt+1=x


Next: Road network extraction
Up: Roads Extraction using a
Previous: Roads Extraction using a
Radu Stoica
2000-04-17
![]() is a measurable space, with measure
is a measurable space, with measure ![]() ,
corresponding
to a uniform Poisson process.
,
corresponding
to a uniform Poisson process.