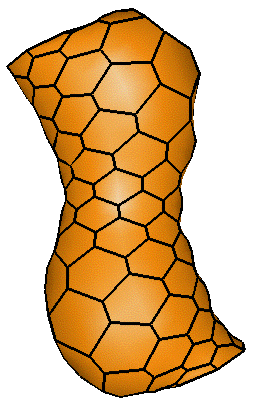
Consider an axial model such as a cylinder or a torus. In the local
framework, if external forces apply on the model, it deforms
localy:

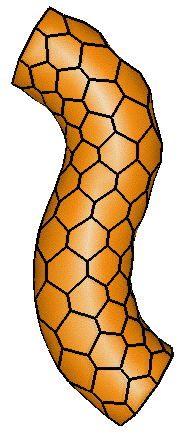
In the hybrid framework, the global constraint applied on the model
may force model vertices to evolve consistantly with the model
axis. We consider that the axis is a 2D deformable contour
with a given rigidity. The external forces applied on vertices
cause the axis to bend and the vertices follow this axis
displacement. Thus we get an axial deformation like:
|
|
|
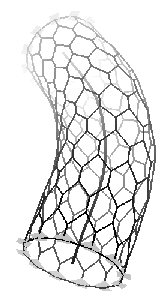
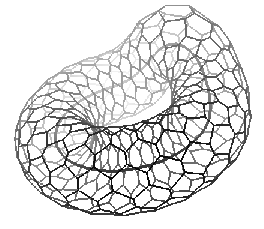
| (a) Cylindrical topology | (b) Toroidal topology | |
When adding an hybrid component to the deformation, it is possible to get localy varying cylinders whose cross sections are not all circular. We illustrate further the axial deformation constraint with a blood vessels segmentation example in angiographic images.