



Next: Second Cauchy theorem
Up: First Cauchy theorem
Previous: Implementation
Contents
Let
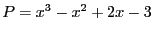 and the procedure:
and the procedure:
Coeff(1)= -3;Coeff(2)=2;Coeff(3)=-1;Coeff(4)=1;
Num=Cauchy_First_Bound_Interval(3,Coeff,Bound);
Coeff_App(1)= INTERVAL(-3.1,-2.9);Coeff_App(2)=INTERVAL(1.9,2.1);
Coeff_App(3)=INTERVAL(-1.1,-0.9);Coeff_App(4)=INTERVAL(0.9,1.1);
Num=Cauchy_First_Bound_Interval(3,Coeff_App,Bound);
In the first case the procedure find that the absolute
value of the roots lie in [0.6,4] while
in the second case the range is [0.58,4.44444].
Jean-Pierre Merlet
2012-12-20